Trees
A tree is a nonlinear data structure, compared to arrays, linked lists, stacks and queues which are linear data structures. A tree can be empty with no nodes or a tree is a structure consisting of one node called the root and zero or one or more subtrees.
Trees can be used to store data that has an inherent hierarchical structure. For example, an operating system may use a tree for directories, files and folders in its file management system. They are dynamic, which means that it is easy to add and delete nodes

Binary Trees
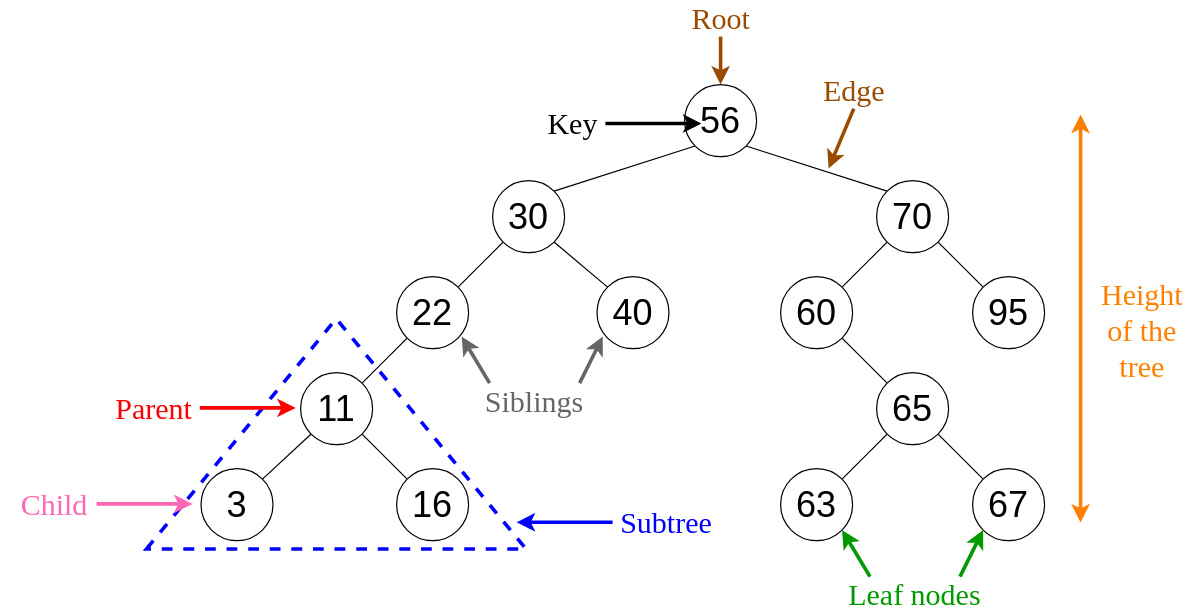
A binary tree is a tree-type non-linear data structure with a maximum of two children for each parent. Every node in a binary tree has a left and right reference along with the data element. … The nodes that hold other sub-nodes are the parent nodes.

Binary Search Trees
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a tree in which all the nodes follow the below-mentioned properties − The value of the key of the left sub-tree is less than the value of its parent (root) node’s key. The value of the key of the right sub-tree is greater than or equal to the value of its parent (root) node’s key.
K-ary Trees
K-ary trees are trees whose internal nodes all have exactly K children. Thus, a full binary tree is a 2-ary tree. The PR Quadtree discussed in Module
is an example of a 4-ary tree. Because K-ary tree nodes have a fixed number of children, unlike general trees, they are relatively easy to implement.
