Access Control (ACL)
%20preview.jpg)
1. When is Basic Authorization used vs. Bearer Authorization?
The Basic and Digest authentication schemes are dedicated to the authentication using a username and a secret (see RFC7616 and RFC7617). The Bearer authentication scheme is dedicated to the authentication using a token and is described by the RFC6750
2. What does the JSON Web Token package do?
A JSON Web Token is used to send information that can be verified and trusted by means of a digital signature. It comprises a compact and URL-safe JSON object, which is cryptographically signed to verify its authenticity, and which can also be encrypted if the payload contains sensitive information
3. What considerations should we make when creating and storing a SECRET?
- Use encryption to store secrets within .git repositorie(keep it protected by saving it in .env file)
- Use environment variables
- Use “Secrets as a service” solutions
- Never store unencrypted secrets in .git repositories
- Avoid git add * commands on git
- Add sensitive files in .gitignore
- Don’t rely on code reviews to discover secrets
- Use automated secrets scanning on repositories
Vocabulary Terms
| Word | Definition |
|---|---|
| Encryption | it is a process that convert our passwords to hashed ones, with characters representation. to make our passwords secured. we use the bcrypt library to do this. |
| Token | used in bearer authentication, a token is a cryptic string that is generated by the server in response to a login request |
| bearer | it is an authorization process, that use the header, and create and compare the token for the users, to allow them to reach a certain endpoints or not. |
| Secret | it is a signature for the developer that make his token secure and no one can access his data when his secret is exists. |
| JSON Web Token | it is an open standard (RFC 7519) that defines a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. |
Preparation Materials
5 steps to RBAC
-
What is RBAC?
RBAC is an approach to restricting system access to authorized users. It is used by the majority of enterprises with more than 500 employees,
-
Benefits of RBAC?
- Access control lists (ACL)
- Attribute-based access control (ABAC)
RBAC implementation
- Inventory your systems
- Analyze your workforce and create roles
- Assign people to roles
- Never make one-off changes
- Audit
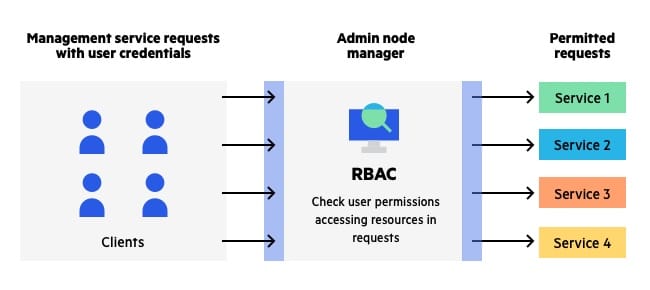
Three primary rules are defined for RBAC
- Role assignment: A subject can exercise a permission only if the subject has selected or been assigned a role.
- Role authorization: A subject’s active role must be authorized for the subject. With rule 1 above, this rule ensures that users can take on only roles for which they are authorized.
- Permission authorization: A subject can exercise a permission only if the permission is authorized for the subject’s active role. With rules 1 and 2, this rule ensures that users can exercise only permissions for which they are authorized.