Tables
The primary purpose of HTML tables is for displaying tabular data in a Web page, that is, information that needs to be displayed in rows and columns.
Tables are also the only reliable way of achieving horizontal alignment of elements using pure HTML.
Basic tables
Tables are divided vertically into rows and horizontally into cells. The contents of the table goes in the cells.
Table cell content can be anything that goes into the body of an HTML document: text, images, links, lists, and even other tables.
HTML tables are set off by table tags:
<table>...</table> which inclose one or more tr (table row) beginning and end tags, like so:
<table> <tr>...</tr> </table> which in turn contain one or more td (table data) beginning and end tags, or optionally th (table header) tags, which set off the cells of the row.
<table> <tr> <td>...</td> </tr> </table> The content of the table is put between these td and th tags. The th tags are used to indicate column or row headers; most browsers therefore display them differently from td tags.
For example, this code
//<table>
//<tr> <th>header one</th> <th>header two</th> </tr>
//<tr> <td>data one </td> <td>data two </td> </tr>
//<tr> <td>data three</td> <td>data four </td> </tr>
//</table> is rendered as [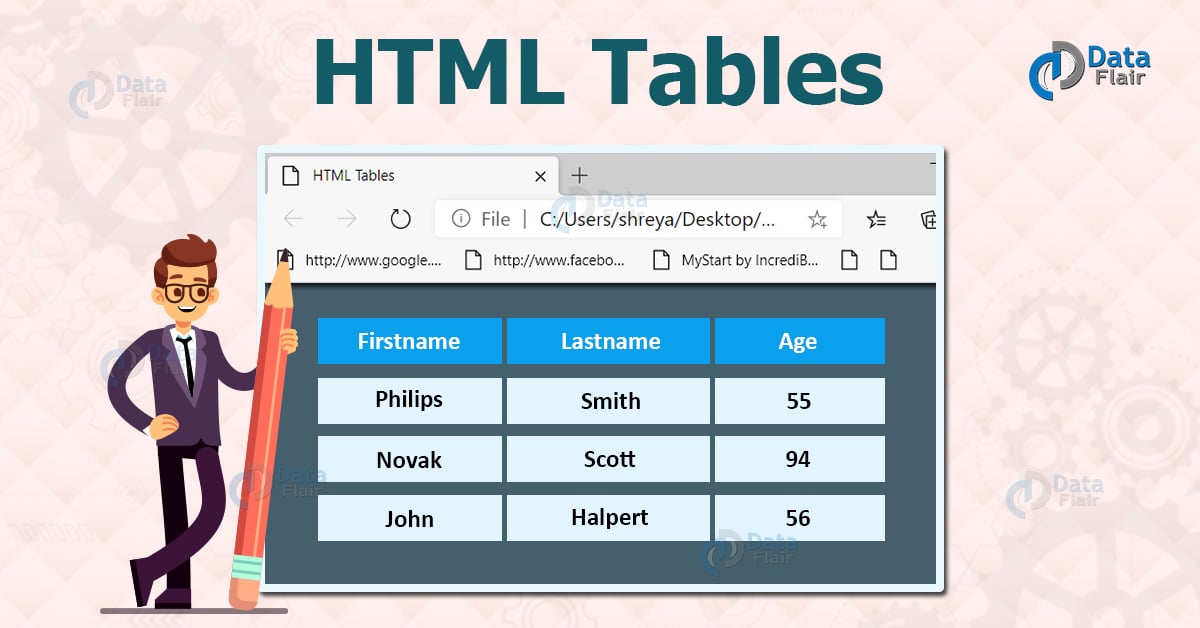]
borders
table frames and cell borders were handled by attributes of the table. This was tricky, and less flexible than the modern CSS styling methods.
borders of the table and its cells are specified by CSS border values. If the border value is “0”, no borders are drawn. The CSS border-left specifies the border to be drawn on the left side, etc. If its value is thin black solid, a thin line border is drawn. There is a variety of border styles besides solid.
Style
Styling, in the sense of formatting, affects tables in two ways.
Generally, style sheets provide a very flexible and convenient means of applying formatting to tables and items within tables. That is, the size and typeface of text, background colors and pictures, etc.
Style sheets have become the standard means of specifying the spacing and widths of table cells, and borders drawn beween them — replacing many table attributes of older versions of HTML.
Styling has also changed the use of tables in HTML. In HTML 3, tables were the only means of providing horizontal alignment in a web page, but modern styles can take over much of this purely presentational role.
A rule of thumb is: use tables for tabular data. Use of tables for alignment of items in a page constitutes breaking the rule “separate presentation from content”, and on these grounds, you should at least try to achieve the effect you want with CSS layout and positioning. Unfortunately, the state of compliance with CSS positioning among one of the most popular web browsers is not great, so your milage may vary.
As always with CSS, it is usually preferred to place style directives in the head block of the HTML code, to separate presentation from content. In the examples that follow therefore, a bit of CSS style will be shown, and then the HTML code that it referrs to.
Function
Everything in JavaScript happens in functions.
A function is a block of code, self contained, that can be defined once and run any times you want.
A function can optionally accept parameters, and returns one value.
Functions in JavaScript are objects, a special kind of objects: function objects. Their superpower lies in the fact that they can be invoked.
In addition, functions are said to be first class functions because they can be assigned to a value, and they can be passed as arguments and used as a return value.
[ ]
]